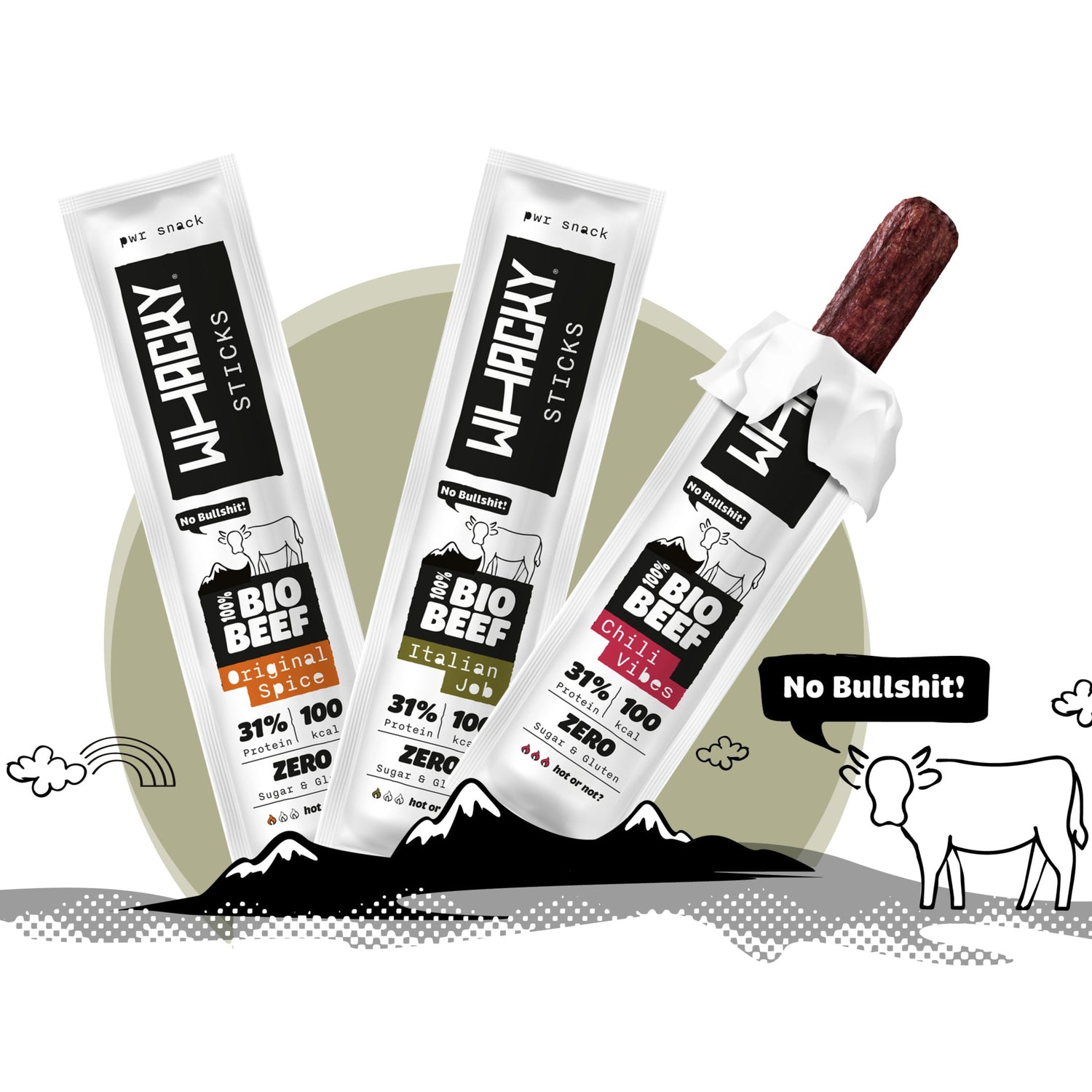
snack smart. stay whacky.
-

10g Bio Protein
-
0g Zucker
-

Allergen-Frei
-
Low Carb
-
-

Keto geeignet
-

leckere Sorten
Filter
-
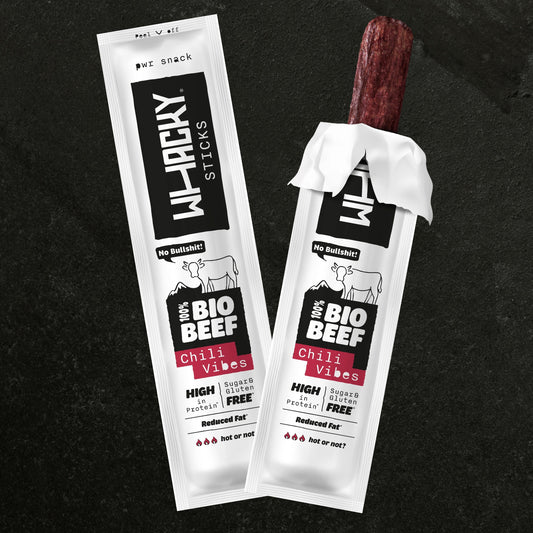
Bio Beef Sticks Probierpaket 3x 32g
142 reviewsSold outRegular price 10,15 €Regular priceUnit price per per€10,15Sale price 10,15 -0%Organic Beef Sticks Mix 9x 32g
58 reviewsSold outRegular price 25,41 €Regular priceUnit price €8,82 per per 100g€30,47Sale price 25,41 -16%€8,82 per 100gSale

Organic Beef Sticks Mix 27x 32g
53 reviewsSold outRegular price 71,17 €Regular priceUnit price €8,24 per per 100g€91,42Sale price 71,17 -22%€8,24 per 100gSaleOrganic Beef Sticks Mix 54x 32g
116 reviewsSold outRegular price 132,18 €Regular priceUnit price €7,65 per per 100g€182,84Sale price 132,18 -27%€7,65 per 100gSale -
Organic Beef Sticks Original Spice 9x 32g
58 reviewsSold outRegular price 25,41 €Regular priceUnit price €8,82 per per 100g€25,41Sale price 25,41 -0%€8,82 per 100gOrganic Beef Sticks Original Spice 30x 32g
116 reviewsSold outRegular price 71,17 €Regular priceUnit price €7,41 per per 100g€84,70Sale price 71,17 -15%€7,41 per 100gSale

Organic Beef Sticks Original Spice 60x 32g
116 reviewsSold outRegular price 132,18 €Regular priceUnit price €6,88 per per 100g€169,40Sale price 132,18 -21%€6,88 per 100gSaleOrganic Beef Sticks Original Spice 90x 32g
116 reviewsSold outRegular price 178,95 €Regular priceUnit price €6,21 per per 100g€254,10Sale price 178,95 -29%€6,21 per 100gSale -
Organic Beef Sticks Italian Job 9x 32g
58 reviewsSold outRegular price 25,41 €Regular priceUnit price €8,82 per per 100g€25,41Sale price 25,41 -0%€8,82 per 100gOrganic Beef Sticks Italian Job 30x 32g
116 reviewsSold outRegular price 71,17 €Regular priceUnit price €7,41 per per 100g€84,70Sale price 71,17 -15%€7,41 per 100gSaleOrganic Beef Sticks Italian Job 60x 32g
116 reviewsSold outRegular price 132,18 €Regular priceUnit price €6,88 per per 100g€169,40Sale price 132,18 -21%€6,88 per 100gSaleOrganic Beef Sticks Italian Job 90x 32g
116 reviewsSold outRegular price 178,95 €Regular priceUnit price €6,21 per per 100g€254,10Sale price 178,95 -29%€6,21 per 100gSale -
Organic Beef Sticks Chili Vibes 9x 32g
116 reviewsSold outRegular price 25,41 €Regular priceUnit price €8,82 per per 100g€25,41Sale price 25,41 -0%€8,82 per 100gOrganic Beef Sticks Chili Vibes 30x 32g
116 reviewsSold outRegular price 71,17 €Regular priceUnit price €7,41 per per 100g€84,70Sale price 71,17 -15%€7,41 per 100gSaleOrganic Beef Sticks Chili Vibes 60x 32g
116 reviewsSold outRegular price 132,18 €Regular priceUnit price €6,88 per per 100g€169,40Sale price 132,18 -21%€6,88 per 100gSaleOrganic Beef Sticks Chili Vibes 90x 32g
116 reviewsSold outRegular price 178,95 €Regular priceUnit price €6,21 per per 100g€254,10Sale price 178,95 -29%€6,21 per 100gSale -
Organic Beef Sticks Original Spice 9x 32g
58 reviewsSold outRegular price 25,41 €Regular priceUnit price €8,82 per per 100g€25,41Sale price 25,41 -0%€8,82 per 100gBio Beef Sticks Smoky Swing 30x 32g
9 reviewsSold outRegular price 71,17 €Regular priceUnit price €7,41 per per 100g€84,70Sale price 71,17 -15%€7,41 per 100gSaleBio Beef Sticks Smoky Swing 60x 32g
9 reviewsSold outRegular price 132,18 €Regular priceUnit price €6,88 per per 100g€169,40Sale price 132,18 -21%€6,88 per 100gSaleBio Beef Sticks Smoky Swing 90x 32g
9 reviewsSold outRegular price 178,95 €Regular priceUnit price €6,21 per per 100g€254,10Sale price 178,95 -29%€6,21 per 100gSale

Ketodiät mit Bio-Beef-Sticks – Wie funktioniert Keto easy?
Begib dich auf ketogene Mission: Mit unseren Bio-Beef-Sticks snackst du dich in Ketose – ohne Krampf! Wenige Kohlenhydrate, moderate Proteine und gesunde Fette – so, wie Keto’s Lehrbuch es verlangt. Hergestellt in Bayern, blitzschnell bei dir, natürlich günstig auf Vorrat. Dein Fettstoffwechsel wird's feiern – ganz ohne Shake-Drama oder Shake-suppe.

Bio Beef-Sticks als Keto-Held – Low Carb & bio – praktisch & perfekt
Wer sagt, Keto muss langweilig sein, hat unsere Keto-Sticks noch nicht probiert! Bio-Rind trifft Bio-Gewürze, null künstliche Zutaten – so schmeckt Keto ohne Kompromisse. Low Carb, nährstoffreich (Zink, Eisen, B-Vitamine), praktisch verpackt, lange haltbar – ideal für unterwegs, fürs Büro oder den Trail. Ketogen genießen war nie bequemer.

Keto-Snack-Guide – So wählst du die besten Beef-Sticks
Nicht jeder Riegel ist gleich keto! Achte auf minimalen Zucker, klare Zutaten und moderate Salzung – dann powert dein Körper optimal in der Ketose. Greif zu Bio-Rind, bleib smart bei der Salzmenge – fertig ist dein Keto-Gamechanger. Unsere Beef-Sticks checken das alles. So bleibst du fokussiert ohne Crash und mit echtem Geschmack.

Schnell zur Ketose – unterwegs & ohne Aufwand
Ketose läuft nicht von allein – du brauchst Snacks, die mitziehen. Unsere Keto-Sticks liefern Protein, Fett und Geschmack im handlichen Format. Kein Mixer, keine Kühlung, kein Stress – nur Reinknabbern. Perfekt für Pendler, Trailblazer, Büro-Ninja oder zackiges Meal-Prep. Und falls dein Snackdruck morgen zuschlägt? Am nächsten Werktag ist Nachschub da.
Kundenstimmen
Let customers speak for us
from 342 reviewsI didn't know the product and I'm glad I tested it. Great quality and I'd buy it again.
Super tasty and very good ingredients
Normally I get heartburn quickly when I eat salami or bifi etc. - not here! It's now the perfect snack for me between meals and tastes really great. Clearly recommended.
The type of packaging, both as a package and the sticks themselves, make a pleasant, professional impression. We had a good feeling throughout.
I wouldn't have thought it, but the taste of the organic beef sticks Italian Job is amazing!😋
Frequently Asked Questions about the Keto Diet
What is keto diet?
Theketo diet(short forketogenic diet) is a diet that is characterized by a very low carbohydrate content and a high fat content. The aim of the diet is to bring the body into a metabolic state calledketosiswhich uses fat instead of carbohydrates as its main energy source.
What are the benefits of a keto diet?
Theketo dietcan provide various benefits depending on a person's individual goals and health. Here are the main potential benefits of the ketogenic diet:
1. Weight loss
2. Stabilization of blood sugar
3. Increase mental clarity and energy
4. Improved fat burning
What should I eat on a keto diet?
At aketo dietThe focus is on foods with high fat content, moderate protein content and very few carbohydrates - especially:
1. Fats & Oils
2. Meat & Fish
3. Eggs
4. Dairy products (in moderation)
5. Vegetables (low-carb)
6. Nuts and seeds
7. Snacks such as our organic beef sticks ;-)
Where can I buy keto snacks?
Here with us! Simply order and just a few days later you can bite into it and enjoy. Enjoy!
Wie funktioniert die Keto-Diät?
Die Keto-Diät reduziert Kohlenhydrate drastisch, um den Körper in Ketose zu bringen – einen Zustand, in dem er Fett anstatt Zucker als Energiequelle nutzt.
Whacky Bio Beef Sticks sind ein idealer Keto-Snack, da sie kaum Kohlenhydrate enthalten und reich an Eiweiß sind.
Wie lange dauert es, bis man in Ketose ist?
In der Regel 2–7 Tage, abhängig von der täglichen Kohlenhydratzufuhr, Bewegung und individueller Stoffwechselrate.
Mit Whacky Bio Beef Sticks fällt der Einstieg leichter, weil sie dich ohne versteckte Zucker satt machen.
Welche Vorteile hat die Keto-Diät?
Zu den Vorteilen zählen oft Gewichtsverlust, ein stabilerer Blutzuckerspiegel, weniger Heißhunger und mehr Energie.
Whacky unterstützt dich dabei mit natürlichen, cleanen Snacks ohne Zusatzstoffe.
Kann man mit der Keto-Diät abnehmen?
Ja – durch den Fettstoffwechsel werden Fettreserven abgebaut, während Eiweiß und Fett satt halten.
Whacky Bio Beef Sticks liefern dir das nötige Eiweiß, um lange satt zu bleiben.
Welche Snacks sind bei Keto erlaubt?
Nüsse, Käse, hartgekochte Eier, Avocado und Fleischsnacks ohne Zucker.
Whacky Bio Beef Sticks sind zuckerfrei, glutenfrei und perfekt für unterwegs.
Gibt es vegetarische oder vegane Keto-Optionen?
Ja, z. B. aus Nüssen, Kokos oder pflanzlichem Eiweiß – jedoch ist die Auswahl begrenzt.
Whacky ist nicht vegan, aber wir setzen auf hochwertiges Bio-Rindfleisch aus nachhaltiger Landwirtschaft.
Ist die Keto-Diät gesund?
Richtig umgesetzt kann sie positive Effekte auf Gewicht und Blutzucker haben. Eine ausgewogene Lebensmittelauswahl ist jedoch wichtig.
Whacky Bio Beef Sticks sind ein gesunder Bestandteil einer ausgewogenen Keto-Ernährung.
Kann man Keto auch langfristig machen?
Viele nutzen Keto als langfristige Ernährungsform, andere als zeitlich begrenzte Kur.
Whacky bietet dir in beiden Fällen Snacks, die sich nahtlos in deinen Plan einfügen.
Kann man Keto unterwegs umsetzen?
Ja – mit Meal-Prep und passenden Keto-Snacks.
Whacky Bio Beef Sticks sind praktisch verpackt, lange haltbar und ideal für Reisen, Arbeit oder Outdoor.
Welche Fehler sollte man bei Keto vermeiden?
Zu viele versteckte Kohlenhydrate, zu wenig Gemüse, zu wenig Elektrolyte und zu wenig Flüssigkeit.
Whacky Bio Beef Sticks helfen dir, versteckte Zucker zu vermeiden.
Sind Whacky Bio Beef Sticks für die Keto-Diät geeignet?
Ja – sie sind kohlenhydratarm, zuckerfrei, glutenfrei und liefern hochwertiges Eiweiß aus Bio-Rindfleisch.
Damit sind sie ein perfekter Keto-Snack für jede Tageszeit.
-
1. Die Keto-Diät verstehen
Die ketogene Diät ist eine kohlenhydratarme, fettreiche Diät, die aufgrund ihrer potenziellen Vorteile bei der Gewichtsabnahme und Verbesserung der allgemeinen Gesundheit an Popularität gewonnen hat. Das Hauptziel der ketogenen Ernährung besteht darin, den Körper über einen bestimmten Ernährungsplan in einen Zustand der Ketose zu versetzen, in dem er Fett anstelle von Kohlenhydraten als Brennstoff verbrennt. Folgende Punkte sind wichtig, damit die Keto-Diät funktioniert:
- Geringe Kohlenhydrataufnahme: Typischerweise begrenzt die Keto-Diät die Kohlenhydrataufnahme auf etwa 20–50 Gramm pro Tag. Diese Reduzierung der Kohlenhydrate trägt dazu bei, die Glykogenspeicher des Körpers zu erschöpfen, was ihn dazu veranlasst, nach alternativen Energiequellen zu suchen.
- Hohe Fettaufnahme: Um die geringe Kohlenhydrataufnahme auszugleichen, fördert die Keto-Diät eine höhere Aufnahme gesunder Fette. Dazu gehören Fette aus Quellen wie Avocados, Nüssen, Samen und Ölen.
- Mäßiger Proteinkonsum: Die Proteinaufnahme wird reduziert, um die Umwandlung von Protein in Glukose zu verhindern, was die Ketose beeinträchtigen kann. Der Schwerpunkt liegt darauf, gerade genug Protein zu sich zu nehmen, um den Muskelerhalt und andere Körperfunktionen zu unterstützen.
-
2. Vorteile der Keto-Diät
Die ketogene Ernährung ist für mehrere potenzielle Vorteile bekannt, darunter:
- Gewichtsverlust: Durch die Umstellung des Stoffwechsels des Körpers von Kohlenhydraten auf Fette kann die Keto-Diät dazu beitragen, den Fettabbau zu beschleunigen.
- Verbesserte Energieniveaus: Viele Menschen berichten von einem stabileren Energieniveau und einer geringeren Müdigkeit, wenn sie eine Keto-Diät befolgen.
- Verbesserte geistige Klarheit: Einige Studien deuten darauf hin, dass Ketose die kognitiven Funktionen und die geistige Klarheit verbessern kann.
- Bessere Blutzuckerkontrolle: Die Keto-Diät kann dazu beitragen, den Blutzuckerspiegel normal zu halten, und hilft so Personen mit Typ-2-Diabetes oder Insulinresistenz.
-
3. Ketogene Ernährung und Diät
Makronährstoffverhältnisse
Die Keto-Diät basiert auf einem bestimmten Makronährstoffverhältnis, um die Ketose aufrechtzuerhalten. Die typische Verteilung ist wie folgt:
Fette: 70–80 % der täglichen Kalorienaufnahme sollten aus Fetten stammen. Dazu gehören einfach ungesättigte Fette, gesättigte Fette und mehrfach ungesättigte Fette.
Proteine: 20–25 % der täglichen Kalorienaufnahme sollten aus Proteinen stammen. Dadurch wird der Muskelerhalt und die Muskelreparatur gewährleistet, ohne dass überschüssige Glukose produziert wird.
Kohlenhydrate: Nur 5–10 % der täglichen Kalorienzufuhr sollten aus Kohlenhydraten stammen. Diese begrenzte Aufnahme ist entscheidend, um den Körper im Zustand der Ketose zu halten.
Essentielle Nährstoffe
Bei einer ketogenen Ernährung ist es wichtig, sicherzustellen, dass du weiterhin wichtige Nährstoffe erhältst, darunter:
- Elektrolyte: Natrium, Kalium und Magnesium sind von entscheidender Bedeutung, da die Keto-Diät zu einem Rückgang dieser Elektrolyte führen kann. Lebensmittel wie Blattgemüse, Avocados und Nüsse können zur Aufrechterhaltung des Elektrolytgleichgewichts beitragen.
- Faser: Trotz des Low-Carb-Fokus sind Ballaststoffe wichtig für die Gesundheit des Verdauungssystems. Integriere kohlenhydratarme, ballaststoffreiche Lebensmittel wie Blattgemüse, Avocados, Leinsamen und Chiasamen.
- Vitamine und Mineralien: Stelle sicher, dass du eine Vielzahl von Lebensmitteln zu dir nimmst, um wichtige Vitamine und Mineralstoffe wie B-Vitamine, Vitamin D, Kalzium und Zink zu erhalten. Lebensmittel wie fetter Fisch, Eier, Käse und kohlenhydratarmes Gemüse sind gute Quellen.
Essensauswahl
Bei der ketogenen Ernährung liegt der Schwerpunkt auf vollwertigen, unverarbeiteten Lebensmitteln. Zu den empfohlenen Speisen gehören:
- Gesunde Fette: Avocados, Nüsse, Samen, Olivenöl, Kokosöl und Butter.
- Proteinquellen: Weiderindfleisch (z. B. aus Bio Beef Sticks), Geflügel, fetter Fisch (wie Lachs und Makrele), Eier und Milchprodukte.
- Low-Carb-Gemüse: Blattgemüse (Spinat, Grünkohl), Brokkoli, Blumenkohl, Zucchini, Paprika und Spargel.
- Getränke: Wasser, Kräutertee und Kaffee ohne Zucker. Als ketofreundliche Optionen können Sie auch Knochenbrühe und Mandelmilch genießen.
-
4. Wie lange dauert es, in die Ketose zu gelangen?
Der Eintritt in die Ketose dauert typischerweise mehrere Tage bis eine Woche und wird von Faktoren wie der Kohlenhydrat- und Proteinaufnahme, dem Aktivitätsniveau, der vorherigen Ernährung und dem individuellen Stoffwechsel beeinflusst.
Schlüsselfaktoren
- Kohlenhydrataufnahme: Die Beschränkung der Kohlenhydrate auf 20–50 Gramm pro Tag beschleunigt die Ketose.
- Proteinaufnahme: Moderate Proteinzufuhr verhindert eine übermäßige Glukoseproduktion.
- Aktivitätslevel: Sport trägt dazu bei, die Glykogenspeicher schneller zu erschöpfen.
- Vorherige Diät: Eine kohlenhydratreiche Ernährung kann den Übergang verlängern.
- Stoffwechsel: Individuelle Stoffwechselraten beeinflussen den Prozess.
Typische Zeitleiste
- Tag 1-2: Der Körper verwendet Glukose aus frischen Kohlenhydraten.
- Tag 2-4: Die Glykogenspeicher erschöpfen sich und es können Symptome der „Keto-Grippe“ auftreten.
- Tag 4-7: Eine erhöhte Ketonproduktion signalisiert den Beginn der Ketose.
Anzeichen einer Ketose
- Vermehrtes Wasserlassen
- Mundtrockenheit und erhöhter Durst
- Mundgeruch (fruchtiger Geruch)
- Reduzierter Appetit
- Erhöhte Energie und geistige Klarheit
- Symptome der Keto-Grippe (Kopfschmerzen, Müdigkeit, Reizbarkeit)
Tipps, um schneller in die Ketose zu gelangen
- Reduziere Kohlenhydrate: Nimm weniger als 20 Gramm Kohlenhydrate pro Tag zu dir.
- Erhöhe gesunde Fette: Versorge deinen Körper mit Fetten.
- Achte auf die Proteinzufuhr: Nimm nur moderat Protein zu dir.
- Sport: betätige dich körperlich.
- Trinken: trinke ausreichend und v.a. Wasser.
- Intermittierende Fasten: Erwäge Intervall-Fasten, um die Ketose zu beschleunigen.
Überwachung der Ketose
- Urinstreifen: Kostengünstig, aber mit der Zeit weniger genau.
- Blutketonmessgeräte: Präzise, aber teurer.
- Atemketonmessgeräte: Nichtinvasiv und praktisch
-
5. Welchen Einfluss hat intermittierendes Fasten auf die Keto-Diät?
Intermittierendes Fasten (IF) ist eine Ernährungsstrategie, die zwischen Essens- und Fastenperioden wechselt. Es kann die ketogene (Keto-)Diät ergänzen und deren Wirksamkeit auf verschiedene Weise steigern:
1. Beschleunigt die Ketose
- Schnellerer Glykogenabbau: Fasten trägt dazu bei, die Glykogenspeicher schneller zu erschöpfen, was den Körper dazu veranlasst, mit der Produktion von Ketonen zur Energiegewinnung zu beginnen.
- Erhöht die Ketonproduktion: Längere Zeiträume ohne Nahrung können den Ketonspiegel im Blut erhöhen und so den Zustand der Ketose verstärken.
2. Verbessert die Fettverbrennung
- Steigert die Stoffwechselrate: Kurzfristiges Fasten kann die Stoffwechselrate steigern und dem Körper helfen, mehr Kalorien und Fett zu verbrennen.
- Fördert die Fettverwertung: Durch einen verringerten Insulinspiegel während des Fastens kann der Körper besser auf gespeichertes Fett zugreifen und es zur Energiegewinnung nutzen.
3. Unterstützt die Gewichtsabnahme
- Kalorienbeschränkung: Intermittierendes Fasten kann auf natürliche Weise zu einer Reduzierung der Gesamtkalorienaufnahme führen und so die Gewichtsabnahme unterstützen.
- Reduziert den Appetit: Fastenperioden können helfen, Hungerhormone wie Ghrelin zu regulieren, den Appetit zu reduzieren und die Einhaltung einer kohlenhydratarmen Diät zu erleichtern.
4. Verbessert die Insulinsensitivität
- Niedrigere Insulinspiegel: Sowohl Keto als auch intermittierendes Fasten tragen dazu bei, den Insulinspiegel zu senken, die Insulinsensitivität zu verbessern und das Risiko für Typ-2-Diabetes zu verringern.
- Verbesserte Glukosekontrolle: Fastenperioden tragen zur Stabilisierung des Blutzuckerspiegels bei und ergänzen den Einfluss der Keto-Diät auf die Reduzierung von Glukosespitzen.
5. Unterstützt Autophagie
- Zellreparatur: Fasten löst Autophagie aus, einen Prozess, bei dem der Körper die alten beschädigten Zellen los wird und neue, gedeihende Zellen bildet, was zu einer besseren allgemeinen Gesundheit führt.
- Reduziert Entzündungen: Autophagie kann helfen, Entzündungen zu reduzieren und die Immunfunktion zu verbessern.
-
6. So kombinierst du intermittierendes Fasten mit der Keto-Diät
Beliebte Methoden des intermittierenden Fastens
- 16/8-Methode: Faste 16 Stunden am Stück und lass 8 Stunden am Tag zum Essen übrig.
- 5:2 Diät: Iss an 5 Tagen in der Woche normal, aber an den anderen beiden Tagen, die nicht aufeinanderfolgende Tage sind, beschränken dich auf etwa 500–600 Kalorien pro Tag
- Essen-Stopp-essen: Faste 24 Stunden am Stück, mache dies 1-2 Mal pro Woche.
- Alternatives Fasten am Tag: Wechsle zwischen normaler Ernährung an einem Tag und Fasten am nächsten Tag.
Beispiel
16/8-Methode:
- Lass das Frühstück aus und iss alle Mahlzeiten zwischen 12 und 20 Uhr.
- Um die Ketose aufrechtzuerhalten, sollten die Mahlzeiten während des Essfensters reich an gesunden Fetten, mäßig proteinhaltig und kohlenhydratarm sein.
-
7. Tipps für den Erfolg
- Trinke genug: Viel Wasser und Tee trinken; Am besten Kräuter- und schwarzen Kaffee in der Fastenzeit, damit der Körper mit Nährstoffen versorgt wird und ihm nicht die Energie ausgeht.
- Überwachen die Elektrolyte: Sorge für eine ausreichende Zufuhr von Natrium, Kalium und Magnesium, um Ungleichgewichte zu vermeiden.
- Höre auf deinen Körper: Pass die Fasten- und Essensfenster an die Reaktion deines Körpers an.
- Allmählicher Übergang: Wenn du neu im intermittierenden Fasten bist, beginne mit kürzeren Fastenperioden und erhöhe die Dauer schrittweise.
- Übertreibe es nicht: Überforde dich nach dem Ende deiner Fastenzeit nicht mit einer großen Menge an Essen, um gesundheitlichen Problemen vorzubeugen.
Beispiel für einen Keto Ernährungsplan
Um dir eine Vorstellung davon zu geben, wie ein typischer Tag einer Keto-Diät aussehen könnte, findest du hier einen detaillierteren Speiseplan:
- Frühstück: Käseomelett mit Spinat, Avocado und Bio Beef Sticks
- Morgensnack: Eine Handvoll Macadamianüsse oder ein Avocado-Smoothie aus ungesüßter Mandelmilch, Spinat und einem Esslöffel MCT-Öl.
- Mittagessen: Gegrillter Hühnersalat mit Whacky Beef Sticks, gemischtem Gemüse, Kirschtomaten, Gurken und Olivenöl-Dressing. Für zusätzliche gesunde Fette mit Feta-Käse und Oliven belegen.
- Nachmittags-Snack: Selleriestangen mit Frischkäse oder Guacamole, oder eine kleine Portion Käse und ein paar Nüsse.
- Abendessen: Gebackener Lachs mit einer Beilage aus geröstetem Brokkoli und Blumenkohl. Mit Olivenöl beträufeln und für zusätzlichen Geschmack mit Parmesankäse bestreuen.
- Nachtisch: Ein paar Beeren mit Schlagsahne (ungesüßt) oder eine kleine Portion dunkle Schokolade (mindestens 70 % Kakao).
Häufige Fallstricke bei der Keto-Ernährung vermeiden
Um den Nutzen der Keto-Diät zu maximieren, ist es wichtig, häufige Fehler zu vermeiden, wie zum Beispiel:
- Zu viel Protein essen: Überschüssiges Protein kann in Glukose umgewandelt werden, was die Ketose stören kann. Pass deine Proteinzufuhr an, um dies zu vermeiden.
- Nicht genügend Ballaststoffe zu sich nehmen: Stelle sicher, dass du ausreichend kohlenhydratarmes, ballaststoffreiches Gemüse zu dir nimmst, um die Verdauungsgesundheit zu unterstützen und Verstopfung vorzubeugen.
- Elektrolyte ignorieren: Ein niedriger Natrium-, Kalium- und Magnesiumspiegel kann zu Symptomen der „Keto-Grippe“ (Kopfschmerzen, Müdigkeit, Reizbarkeit) führen. Stelle sicher, dass du diese Elektrolyte nach Bedarf ergänzt.
Wie passen Rindfleischsticks in die Keto-Diät?
Rindersticks sind aus mehreren Gründen eine ausgezeichneter Keto Snack für diejenigen, die eine ketogene Diät einhalten:
Kohlenhydratarm
Rindersticks sind von Natur aus kohlenhydratarm und eignen sich daher für eine Keto-Diät. Mit einem Minimum an Kohlenhydraten tragen sie dazu bei, den Zustand der Ketose aufrechtzuerhalten, sodass der Körper weiterhin Fett zur Energiegewinnung verbrennen kann. Dieser kohlenhydratarme Gehalt ist entscheidend für jeden, der in der Ketose bleiben möchte, ohne Kompromisse bei Geschmack und Bequemlichkeit einzugehen.
Reich an Protein
Während bei der Keto-Diät der Schwerpunkt auf einer hohen Fettaufnahme liegt, ist auch ein moderater Proteinkonsum von entscheidender Bedeutung. Rindersticks liefern eine gute Menge an Protein, das für den Muskelerhalt und die allgemeinen Körperfunktionen unerlässlich ist. Sie sind der perfekte Keto-Riegel. Es ist jedoch wichtig, nicht zu viele Proteine zuzuführen, um eine Störung der Ketose zu vermeiden. Das Protein in Rindfleischstäbchen hat außerdem eine hohe Bioverfügbarkeit, was bedeutet, dass es vom Körper effizient genutzt wird und somit eine ausgezeichnete Quelle für essentielle Aminosäuren ist, die für die Muskelreparatur und das Muskelwachstum benötigt werden.
Reich an gesunden Fetten
Einige Rindfleischstäbchen werden mit einem höheren Fettgehalt hergestellt, was gut mit dem Bedarf der ketogenen Ernährung an einem erhöhten Fettkonsum übereinstimmt. Diese gesunden Fette können dazu beitragen, dass du satt bleibst und eine stetige Energiequelle hast. Hochwertige Rindersticks enthalten oft Fette aus natürlichen Quellen, die bei der Keto-Diät zu bevorzugen sind. Der Fettgehalt trägt dazu bei, das Sättigungsgefühl zu fördern, Heißhungerattacken zu reduzieren und das Energieniveau den ganzen Tag über aufrechtzuerhalten.
Praktisch - auch für unterwegs
Eine der Herausforderungen bei einer Keto-Diät besteht darin, praktische Snacks zu finden, die zum Makronährstoffprofil der Diät passen. Unsere Bio Beef Sticks sind tragbar, erfordern keine Zubereitung und sind leicht zu transportieren, was sie zu einem idealen Snack für vielbeschäftigte Menschen mit Keto-Diät macht. Egal, ob du auf Reisen, bei der Arbeit oder bei Outdoor-Aktivitäten bist, Beef Sticks sind eine praktische Option, die deine Ernährungszielen helfen. Mit ihrer praktischen recyclingfähigen Verpackung hast du immer einen ketofreundlichen Snack zur Hand, sodass du nicht zu kohlenhydratreichen Alternativen greifen musst.
Nährstoffreich
Beef Sticks sind nicht nur kohlenhydratarm und reich an Proteinen und Fett, sondern auch reich an essentiellen Nährstoffen wie Zink, Eisen und B-Vitaminen. Diese Nährstoffe sind wichtig für die allgemeine Gesundheit und können dazu beitragen, den Nährstoffbedarf von Menschen zu decken, die sich ketogen ernähren. Zink spielt eine wichtige Rolle bei der Immunfunktion und der Proteinsynthese, während Eisen für den Sauerstofftransport im Blut entscheidend ist. B-Vitamine unterstützen die Energieproduktion und die Gehirnfunktion und machen Rindfleischsticks zu einer nährstoffreichen Ergänzung deines Keto-Speiseplans.
-
8. Auswahl der richtigen Beef Sticks für deine Keto-Diät
Wenn Du Beef Jerky bzw. Beef Sticks oder auch Salami Sticks also Keto Snacks für deine Keto-Diät verwenden möchtest, ist folgendes zu berücksichtigen:
- Überprüfe die Zutaten: Suche nach Beef Sticks mit minimalem Zuckerzusatz und vermeiden solche mit hohem Kohlenhydratgehalt. Entscheide dich für Produkte mit einer sauberen Zutatenliste, frei von unnötigen Füllstoffen und künstlichen Zusatzstoffen.
- Wähle hochwertige Zutaten: Entscheide dich für Beef Sticks aus grasgefüttertem Rindfleisch oder aus biologischem Anbau, um sicherzustellen, dass du die beste Qualität erhältst. Biologisch grasgefüttertes Rindfleisch enthält im Vergleich zu mit Getreide gefüttertem Rindfleisch häufig mehr Omega-3-Fettsäuren und Antioxidantien.
- Achte auf den Natriumgehalt: Während etwas Natrium notwendig ist, können zu hohe Mengen ungesund sein. Wähle daher Beef Sticks als deine Ketoriegel, die sich durch einen mäßigem Natriumgehalt auszeichnen. Es ist auch von Vorteil, die Natriumaufnahme mit anderen Elektrolyten auszugleichen, insbesondere wenn du aktiv bist oder zum Schwitzen neigst.
9. Zusammenfassung
Rindfleischsticks sind eine fantastische Ergänzung zu einer Keto-Diät und bieten eine praktische, kohlenhydratarme, proteinreiche und nährstoffreiche Snackoption in deinem Ernährungsplan. Egal, ob du unterwegs bist oder einen schnellen und einfachen Snack suchst, Rindfleischsticks können dir dabei helfen, deine Keto-Ziele einzuhalten, während sie gleichzeitig wichtige Nährstoffe liefern und deinen Hunger stillen. Nutze die Vorteile von Beef Sticks und genieße einen köstlichen, ketofreundlichen Snack, der deinen gesunden Lebensstil unterstützt.
Der Eintritt in die Ketose dauert in der Regel 3–7 Tage und kann beschleunigt werden, indem man die Kohlenhydratzufuhr einschränkt, gesunde Fette erhöht, Proteine mäßigt und aktiv bleibt. Die Überwachung des Ketonspiegels hilft dabei, den Fortschritt zu verfolgen, während intermittierendes Fasten die Fettverbrennung weiter fördert, die Gewichtsabnahme unterstützt und die Insulinsensitivität verbessert. Die Kombination dieser Strategien optimiert die Gesundheit und hilft beim Erreichen von Gewichts- und Fitnesszielen.
Durch die Integration von Rindfleischstäbchen in deinen Keto-Diät kannst du einen leckeren, praktischen und nahrhaften Snack genießen, der perfekt zu deinen Ernährungsbedürfnissen passt.
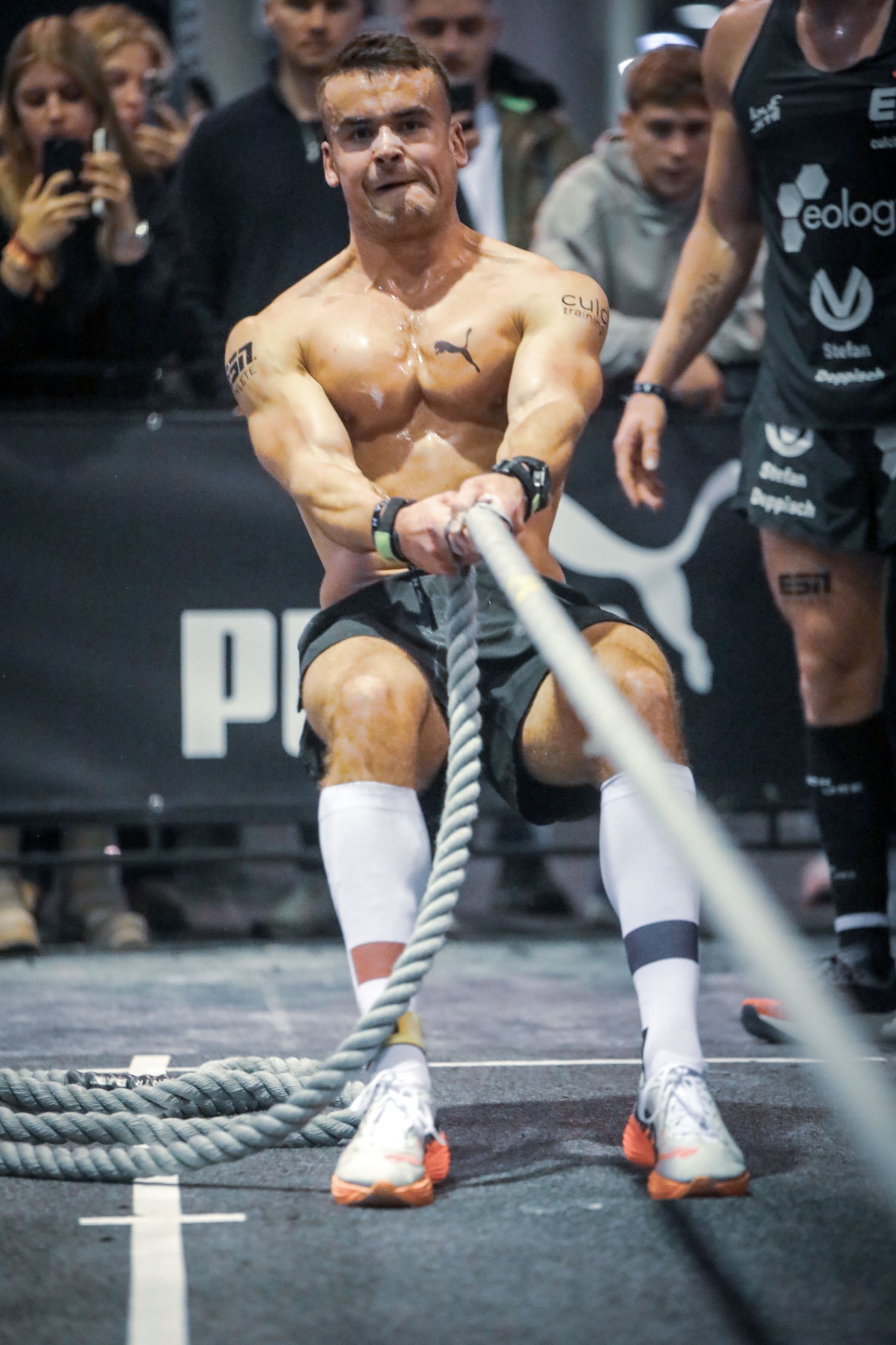

HYROX Weltmeister Jannik Czapla - offizieller Partner von Whacky
"Disziplin, Ehrgeiz und Bio Beef Sticks - die perfekte Kombination, um mein Potenzial zu entfalten."
Jannik, HYROX Elite Double Weltmeister






















